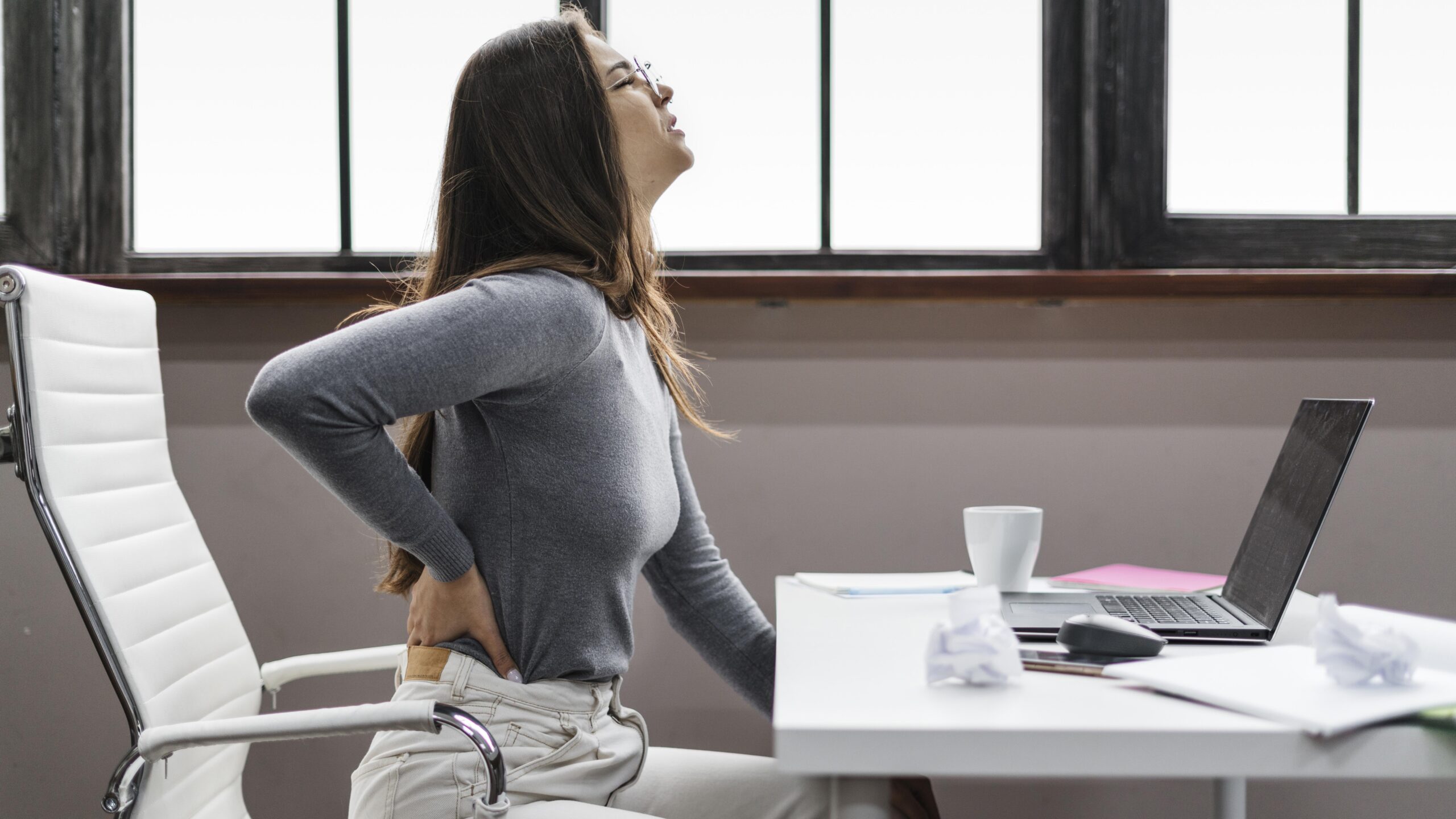
Lower back pain is one of the most common medical conditions that affects people worldwide. Whether it’s a dull, nagging ache or a sharp, debilitating pain, lower back pain can severely affect your daily life, making even simple tasks like sitting, walking, or lifting a challenge. According to studies, up to 80% of adults will experience lower back pain at some point in their lives. The good news is that there are a wide variety of lower back pain treatment options available to help you manage, reduce, and even eliminate discomfort.
This comprehensive guide will explore the most effective treatments for lower back pain, from conservative approaches to advanced therapies, helping you find the best solution for your unique situation. Whether you are dealing with acute pain due to an injury or chronic pain from conditions like arthritis or degenerative disc disease, understanding your treatment options is the first step toward lasting relief.
1. Understanding Lower Back Pain: Causes and Symptoms
Before diving into treatment options, it’s important to understand the causes of lower back pain and the types of symptoms that may accompany it. Lower back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Muscle Strains and Sprains: Overuse or improper movement can strain the muscles and ligaments in the lower back, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Herniated or Bulging Discs: When the soft, gel-like discs between the vertebrae bulge or rupture, they can press on nearby nerves, causing sharp pain, numbness, or tingling.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: As we age, the discs in the spine can lose their cushioning ability, leading to chronic pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition involves the narrowing of the spaces within the spine, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
- Sciatica: When the sciatic nerve is compressed, it can lead to pain that radiates down the leg.
- Poor Posture: Prolonged poor posture, whether from sitting at a desk or standing incorrectly, can lead to misalignment in the spine, which can cause pain.
Symptoms of lower back pain may include:
- Dull or sharp pain in the lower back
- Stiffness or tightness in the muscles
- Numbness or tingling down the leg (especially with sciatica)
- Difficulty standing, walking, or sitting for prolonged periods
- Pain that worsens with certain movements, such as bending or twisting
2. Conservative Treatments for Lower Back Pain
For most people, lower back pain treatment begins with conservative, non-invasive approaches. These treatments aim to reduce pain, improve mobility, and promote healing without the need for surgery or medications. Here are some of the most effective conservative treatments:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is one of the most effective long-term treatments for lower back pain. A physical therapist will design a customized exercise program to strengthen the muscles supporting the lower back, improve flexibility, and correct any postural issues that may be contributing to your pain. Key components of physical therapy for back pain include:
- Strengthening Exercises: Building strength in the core muscles (abdominals, back, and hips) helps stabilize the spine and reduce the load on the lower back.
- Stretching: Stretching exercises increase flexibility, helping to relieve tension and improve mobility in the muscles and joints.
- Posture Correction: Proper posture is essential for preventing and relieving lower back pain. Physical therapists can teach you techniques for sitting, standing, and moving correctly.
- Manual Therapy: Some physical therapists use hands-on techniques to manipulate the spine and joints, which can help alleviate stiffness and pain.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care is another popular lower back pain treatment that focuses on spinal health. Chiropractors use spinal manipulation (also called spinal adjustments) to restore proper alignment to the spine and relieve pain. This treatment is based on the belief that misalignments in the spine can interfere with the nervous system and cause pain and dysfunction.
Chiropractic adjustments can provide the following benefits:
- Pain Relief: Spinal adjustments can reduce inflammation, ease muscle tension, and improve joint function, providing significant pain relief.
- Increased Mobility: Realigning the spine helps improve mobility, allowing for greater flexibility and range of motion in the back and surrounding areas.
- Non-Invasive: Chiropractic care is a non-surgical treatment option, making it a safe and effective alternative for those seeking relief without medication or surgery.
Chiropractic care can be particularly helpful for individuals with musculoskeletal lower back pain, but it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if it’s the right choice for you.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Non-prescription medications can be helpful for managing lower back pain on a short-term basis. The most commonly used over-the-counter (OTC) medications include:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) are effective at reducing inflammation and relieving pain.
- Acetaminophen: Drugs like Tylenol can help manage pain but do not address inflammation.
These medications should be used with caution, as prolonged use can lead to side effects like stomach ulcers or liver damage. Always follow the recommended dosages and consult with your doctor if you require long-term pain relief.
Hot and Cold Therapy
Using heat or cold on the lower back is a simple and effective way to reduce pain and inflammation. Applying cold compresses (such as an ice pack) can reduce inflammation and numb the area, while heat therapy (such as a heating pad or warm bath) can help relax tight muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area.
It’s important to use these therapies properly:
- Cold Therapy: Apply for 15–20 minutes at a time, especially within the first 48 hours after an injury.
- Heat Therapy: Use heat after the initial inflammation has gone down (usually after 48 hours) to soothe muscles and improve flexibility.
3. Advanced Treatments for Lower Back Pain
If conservative treatments don’t provide sufficient relief, more advanced options may be necessary to manage your lower back pain. These treatments are typically used for more severe or chronic pain conditions.
Injections for Pain Relief
For those with persistent pain that does not respond to physical therapy or medication, spinal injections can offer targeted relief. Some common types of injections include:
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These injections deliver corticosteroids directly to the epidural space around the spinal cord. They help reduce inflammation and relieve pain, particularly in conditions like sciatica or herniated discs.
- Facet Joint Injections: These are used to treat pain caused by inflammation of the facet joints in the spine. The injection contains an anesthetic and steroid to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Nerve Blocks: For nerve-related pain, nerve blocks can be injected to prevent pain signals from reaching the brain.
While these injections can provide relief, they are typically used as part of a broader pain management strategy and are not a long-term solution.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat chronic lower back pain, especially when it’s caused by arthritis or damaged facet joints. During RFA, a needle is inserted near the nerves causing pain, and radiofrequency waves are used to heat and destroy the nerve tissue, reducing pain transmission.
This procedure is generally safe, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief for several months to years.
Surgical Options
In cases of severe, debilitating pain or when non-surgical treatments have not been successful, surgery may be necessary. Surgical options are typically reserved for conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. Some common surgical procedures include:
- Discectomy: Removal of part or all of a herniated disc to relieve nerve pressure.
- Spinal Fusion: Joining two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine and prevent further damage.
- Laminectomy: Removal of part of the vertebra (the lamina) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
While surgery can be highly effective, it carries risks, including infection, nerve damage, and long recovery times. Surgery is usually considered a last resort after all other treatment options have been exhausted.
4. Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Lower Back Pain
In addition to medical treatments, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent lower back pain and improve your overall well-being. Some key lifestyle changes to consider include:
- Regular Exercise: Strengthening your core muscles, improving flexibility, and maintaining a healthy weight can help support your spine and prevent future pain.
- Maintain Good Posture: Be mindful of your posture when sitting, standing, and lifting. Use ergonomic furniture, and take breaks from sitting to avoid strain on your back.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking can impede blood flow and reduce the oxygen supply to spinal tissues, contributing to back pain.
- Stay Active: Avoid long periods of inactivity. Gentle activities like walking or swimming can help keep the spine healthy and reduce stiffness.
5. When to Seek Professional Help
While mild lower back pain can often be treated at home with rest, ice, and over-the-counter medications, it’s important to seek professional help if:
- The pain persists for more than a few weeks or becomes progressively worse.
- You experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in your legs.
- Pain is accompanied by bladder or bowel problems.
- You have a history of cancer, osteoporosis, or other serious conditions.
A healthcare professional can assess your condition, identify the underlying cause of your pain, and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Lower back pain is a common and often debilitating condition, but with the right treatment, you can find relief and regain control of your life. From conservative treatments like physical therapy and chiropractic care to advanced options like injections and surgery, there are a variety of solutions available to help you manage your pain.
By combining the right treatment with lifestyle changes such as exercise, good posture, and healthy habits, you can not only alleviate lower back pain but also prevent it from returning. If you’re dealing with chronic or severe back pain, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your needs.