Train ambulance services have emerged as a crucial component in India’s healthcare transportation network, especially in regions where traditional road ambulances face accessibility challenges. As one of the most populous and geographically diverse nations in the world, India benefits immensely from a multi-layered medical transportation system, with train ambulances playing an increasingly vital role. This article delves into the recent innovations, government policies, and future improvements that could shape the trajectory of train ambulance services in India, ensuring faster and more efficient medical care for remote and underserved populations.
1. The Importance of Train Ambulance Services in India
In a country with over 1.4 billion people spread across urban, semi-urban, and rural landscapes, rapid medical response is essential but often challenging. Train ambulances, with their capacity to cover vast distances more quickly and consistently than road vehicles, serve as a lifeline for patients requiring emergency medical care or transport to specialized facilities in metropolitan areas. Unlike air ambulances, which are limited by higher costs and weather conditions, train ambulances provide a more economical and reliable solution for long-distance patient transfer, particularly for cases where air transport isn’t feasible.
2. Key Innovations in Train Ambulance Services
Recent technological advancements have greatly improved the efficiency and effectiveness of train ambulance services in India. These innovations not only ensure better patient outcomes but also make the service more viable and accessible to a larger portion of the population.
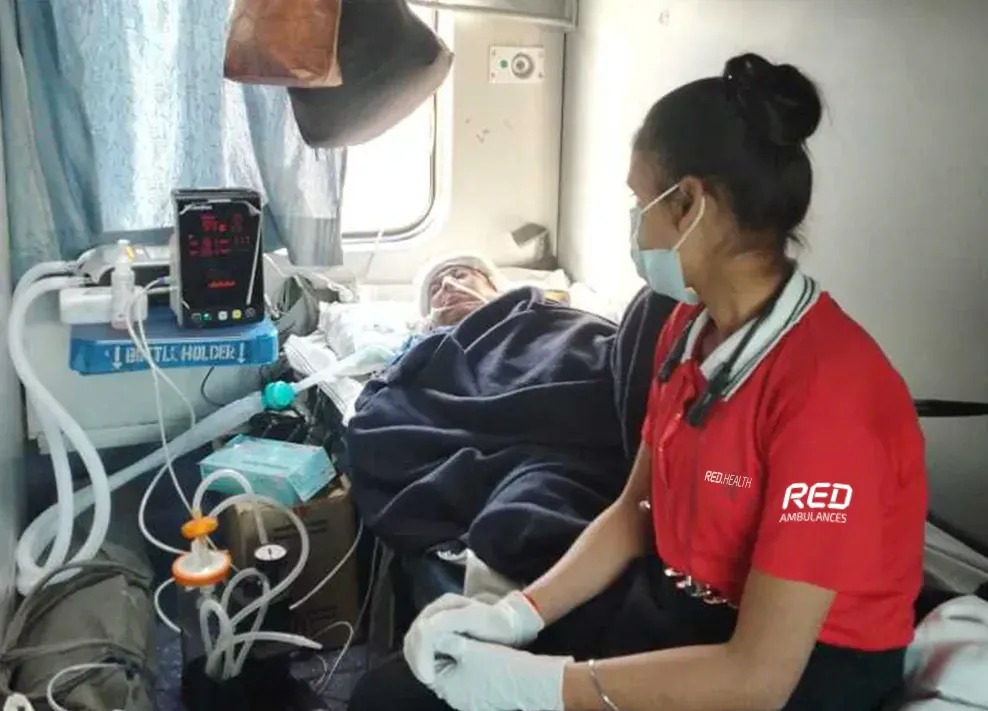
a. Onboard Medical Infrastructure
Modern train ambulances now come equipped with critical care infrastructure similar to what one would find in an intensive care unit (ICU). This includes ventilators, defibrillators, infusion pumps, oxygen supply systems, and other life-support equipment, allowing stable as well as critically ill patients to be safely transported for hours or even days. Dedicated compartments are modified to ensure adequate space for patient monitoring, medical intervention, and easy movement of medical personnel during transit.
b. Telemedicine Integration
Telemedicine has become a valuable addition to train ambulance services. By integrating telemedicine equipment and providing real-time communication with doctors at destination hospitals, medical staff on board can receive continuous guidance on patient management. This enables them to make timely adjustments to treatment, thereby reducing complications and improving survival rates during transit.
c. AI-Powered Monitoring Systems
With advancements in artificial intelligence, some train ambulances have started to implement AI-powered health monitoring systems. These systems continuously assess vital signs and predict potential health issues before they escalate, sending alerts to medical staff to take preventive action. Such technologies help mitigate risks during long-distance transfers and ensure proactive patient care.
d. Enhanced Communication Networks
One of the biggest challenges for any mobile medical service is maintaining continuous communication. Upgraded communication networks, supported by the rollout of 5G in many regions, are significantly enhancing connectivity for train ambulances. These networks ensure real-time data transfer, enabling healthcare professionals at the receiving hospital to prepare based on the patient’s condition before arrival. In emergency medical services, every second counts, and these advancements help save valuable time.
3. Policies Driving Train Ambulance Services
Government policies have played a crucial role in supporting and expanding train ambulance services in India. Various initiatives and regulatory frameworks aim to improve healthcare accessibility, particularly for rural and underserved populations.
a. National Health Mission (NHM)
The NHM has consistently worked toward improving healthcare accessibility across the country, including establishing train ambulances in remote areas. Collaborations between the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and Indian Railways have been instrumental in funding and implementing train ambulance services for inter-state patient transfer.
b. Subsidies and Funding Support
Government subsidies and financial assistance have made it easier for private players to operate train ambulances, reducing the overall cost of transportation for patients. This has helped make the service more affordable, especially for economically disadvantaged individuals.
c. Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Regulations
Regulatory frameworks for EMS have established standards for medical equipment, staffing, and protocols, ensuring a high level of care on board train ambulances. These regulations also include periodic training for EMS personnel, preparing them to handle a variety of medical emergencies during transit.
4. Potential Improvements for the Future
While the current train ambulance service system in India has made impressive strides, there is room for further development to ensure more effective and comprehensive patient care.
a. Expanding Service Coverage
Most existing train ambulance services operate between major cities or metropolitan areas, often leaving remote regions with limited access to these critical services. Expanding service routes to include more regional stations would greatly enhance the reach and utility of train ambulances.
b. Increased Private Sector Involvement
Involving private players in the train ambulance sector can drive innovation and competition, potentially leading to cost reduction and improved quality of services. Partnerships between government bodies and private companies can help scale services more quickly, ensuring that more regions and populations are covered.
c. Developing Specialized Medical Units
Certain medical conditions, such as severe trauma or advanced cardiac care, require highly specialized attention during transportation. Developing specific compartments or units within train ambulances that cater to particular medical needs—such as neonatal or pediatric ICUs—would be a valuable addition, ensuring tailored care for diverse patient groups.
d. Improving Patient Transfer Protocols
Efficient patient handover protocols are essential to maintain continuity of care when patients arrive at their destination hospitals. Implementing standardized transfer protocols for all train ambulance services, with pre-notified medical teams ready for patient reception, would help reduce the time from arrival to treatment, improving outcomes.
e. Leveraging Data Analytics for Route Optimization
Data analytics can be utilized to optimize travel routes and schedules for train ambulances, ensuring patients reach their destinations in the shortest time possible. By analyzing historical data on train speeds, traffic, and time delays, the railways can develop models that allow real-time adjustments to travel routes, ultimately reducing patient transfer times.
Conclusion
Train ambulances hold immense potential for the future of healthcare in India, particularly in connecting rural and remote populations with critical medical services. With further advancements in technology, greater government support, and a growing interest from private stakeholders, the sector is poised for significant growth. These services not only enhance the scope of emergency medical response but also bring a new dimension of connectivity to India’s healthcare landscape. Organizations like RED.health are instrumental in bridging the gaps within this landscape, driving innovation and operational support to ensure that train ambulance services reach those who need them the most. As the sector evolves, the continued integration of policies, technology, and collaborative initiatives will make train ambulance services a cornerstone of India’s emergency medical infrastructure.