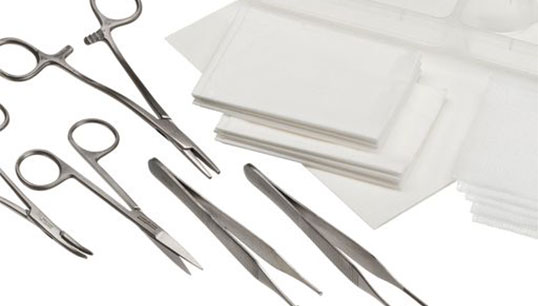
Single use surgical instruments play a crucial role in modern healthcare practices. Designed for one-time use, these instruments provide a level of safety and hygiene that is essential in surgical environments. As the medical industry continues to evolve, the adoption of single-use instruments is becoming increasingly common, driven by the need to minimize the risk of infection and ensure patient safety. This article will delve into the types, benefits, and considerations of single-use surgical instruments, shedding light on why they are a vital component of contemporary surgical procedures.
The growing emphasis on infection control and patient safety has led to the increased utilization of single-use surgical instruments across various medical disciplines. These instruments help eliminate the risk of cross-contamination, making them an appealing choice for healthcare providers. Understanding the significance of these instruments is essential for both medical professionals and patients alike.
Benefits of Single Use Surgical Instruments
- Infection Control: One of the primary advantages of single-use surgical instruments is their ability to reduce the risk of infections. Since these instruments are used only once and then disposed of, there is no chance of cross-contamination between patients. This is especially crucial in surgical settings where maintaining a sterile environment is paramount.
- Convenience: Single-use instruments offer convenience for healthcare providers. They arrive sterile and ready for use, eliminating the need for reprocessing and sterilization. This can save valuable time in busy surgical settings, allowing medical staff to focus on patient care rather than instrument maintenance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While single-use instruments may have a higher upfront cost compared to reusable instruments, they can be more cost-effective in the long run. The elimination of sterilization processes, labor costs associated with reprocessing, and the reduced risk of surgical site infections can lead to significant savings for healthcare facilities.
- Quality Assurance: Manufacturers of single-use surgical instruments adhere to stringent quality control measures to ensure that their products meet high standards. This level of oversight can result in more reliable and consistent instruments, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
- Variety of Options: The market for single-use surgical instruments has expanded significantly, offering a wide variety of options to suit different surgical needs. From scalpels and scissors to forceps and clamps, healthcare providers have access to an extensive range of instruments that can be tailored to specific procedures.
Types of Single Use Surgical Instruments
Single-use surgical instruments come in various types, each designed for specific functions in the operating room. Some common categories include:
- Scalpels: Used for making incisions, single-use scalpels are sharp and precise, ensuring clean cuts during surgery.
- Forceps: These instruments are used for grasping and holding tissues or objects during surgical procedures. Single-use forceps come in different designs to accommodate various surgical needs.
- Scissors: Single-use surgical scissors are designed for cutting tissues, sutures, or other materials during surgery. Their sharp blades ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Needles and Syringes: Single-use needles and syringes are essential for administering medications or anesthetics during surgical procedures. Their sterile nature reduces the risk of infection.
- Electrosurgical Instruments: These instruments use electrical currents to cut or coagulate tissues during surgery. Single-use versions are available to ensure sterility and effectiveness.
Considerations for Using Single Use Surgical Instruments
While single-use surgical scissors offer numerous benefits, there are several considerations to keep in mind:
- Environmental Impact: The disposal of single-use instruments can contribute to medical waste, raising environmental concerns. Healthcare facilities should implement proper waste management practices to minimize their ecological footprint.
- Cost Analysis: Although single-use instruments can be cost-effective in terms of infection control and labor savings, healthcare providers must conduct a thorough cost analysis to determine their overall financial impact.
- Supply Chain Management: Ensuring a consistent supply of single-use instruments is essential for uninterrupted surgical operations. Healthcare facilities must establish reliable relationships with manufacturers and suppliers to maintain an adequate inventory.
- Regulatory Compliance: The use of single-use surgical instruments is subject to regulations and guidelines set by healthcare authorities. Providers must stay informed about compliance requirements to ensure patient safety and legal adherence.
- Staff Training: Healthcare staff should receive training on the proper use and disposal of single-use instruments. This ensures that instruments are used effectively and that safety protocols are followed.
Summery
Single-use surgical instruments are an integral part of modern surgical practices, offering significant advantages in terms of infection control, convenience, and patient safety. As the healthcare industry continues to prioritize patient outcomes, the adoption of single-use instruments is likely to grow. Understanding their benefits, types, and considerations can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about incorporating these instruments into their surgical protocols. As a patient, being aware of the use of single-use surgical instruments can provide peace of mind during medical procedures. Knowing that your healthcare provider is committed to maintaining a sterile environment and minimizing the risk of infection is reassuring. By embracing single-use surgical instruments, both patients and providers can work together to ensure safer surgical experiences and improved healthcare outcomes.